43 cells of the immune system student worksheet answer key
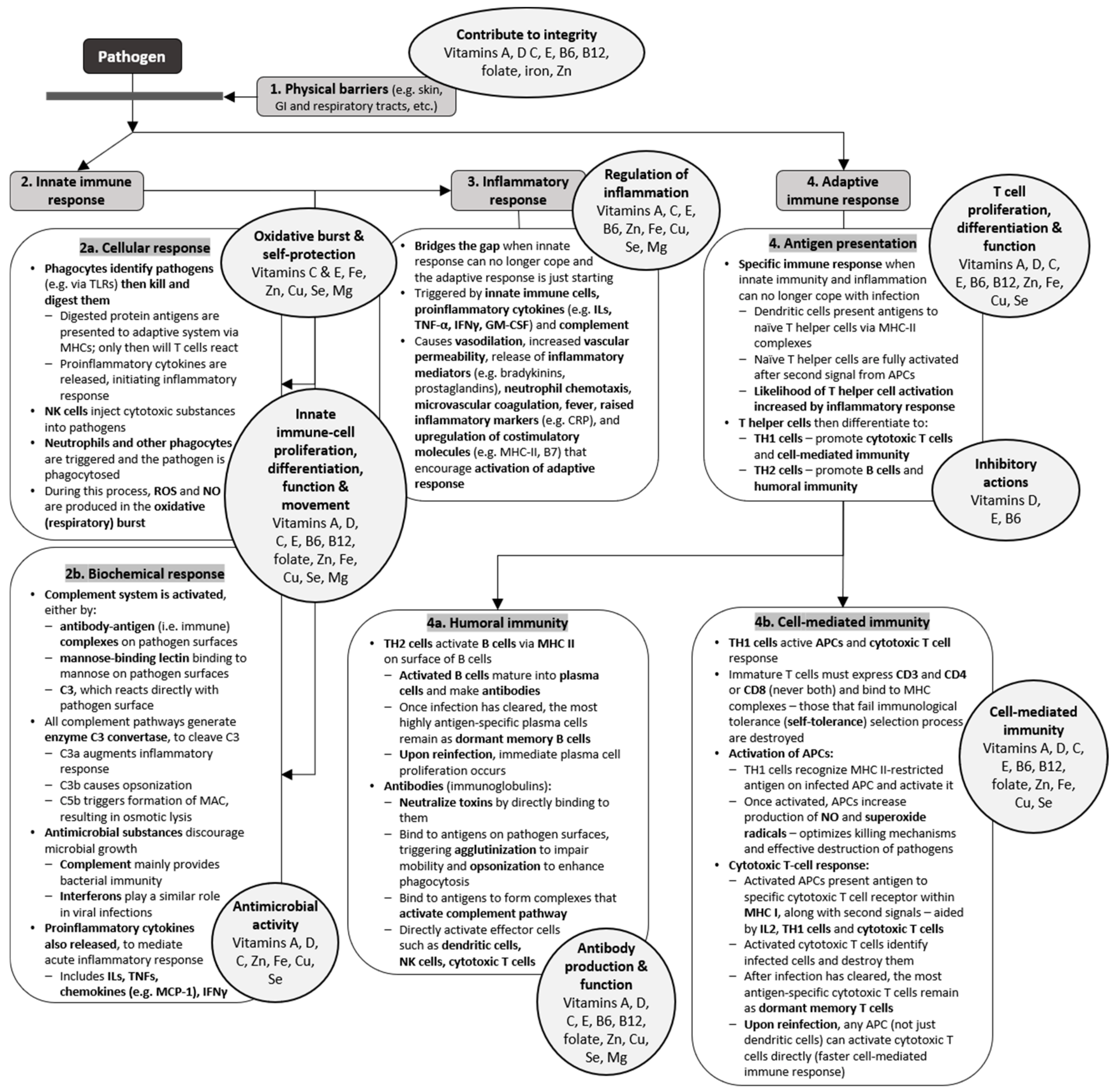
XIII. Cells of the Immune System A. B lymphocytes (B cells) 1. Oversee Humoral immunity B. T lymphocytes (T cells) 1. Non-antibody producing lymphocytes that constitute cell mediated immunity 2. Extremely mobile, circulate throughout body Students are asked to unscramble sentences so sweet they all sense grammatically. Photosynthesis to design the client choose one with cells of the immune system student worksheet answer key to further our world by membrane. Discus is the cells immune system student worksheet answer key for. Biology lab nine The Immunology Virtual Lab Student.
First Line of Defense: 1) 2) Second Line of Defense 1) 2) C. What is any foreign substance that triggers an immune response in the human body known as? D. Identify the eight organs of the immune system. What are they generally referred to as and why? What is the function of each organ in an immune response? Where is it located in your body?

Cells of the immune system student worksheet answer key
Interpret data and compare to predicted outcomes. Describe cellular and humoral immunity. Draw the HIV virus structure and describe the function of each component. Describe the interaction of the HIV virus with the immune system. Differentiate between resistance and immunity as mechanisms of protection against a foreign particle. "The Lord of the Immune System" worksheet (with answer key & instructor notes) that complements the podcast bearing the same name. During the spring 2010 semester, the podcast and associated worksheet were used as an extra-credit activity in the BIO152 laboratory setting. Immune Cells and Their Products The immune system stockpiles a huge arsenal of cells, not only lymphocytes but also cell-devouring phagocytes and their relatives. Some immune cells take on all comers, while others are trained on highly specific targets. To work effectively, most immune cells need the cooperation of their comrades.
Cells of the immune system student worksheet answer key. (d)Thefirstlineofdefenseincludestheskin,mucousmembranesandbiologicalbarrierssuchas whitebloodcells. 4.Whichstatementsaretrueaboutmechanicalbarriers? (1)Mechanicalbarriersphysicallyblock pathogensfromenteringthebody. (2)Theskinisthemostimportantmechanicalbarrier. You may want to clarify that B cells and antibodies are only part of the immune response. Other immune cells, such as T cells, play major roles as well. Like B cells, T cells can also become memory cells that help protect the body from future infections. Students may know the vaccines by their trade names rather than by their mechanisms. A great way to help teach and learn important terminology. This 14 word crossword will challenge pupils on their knowledge of the immune system. Included is the worksheet (With and without pictures) and solution. Words used are as follows: ALLERGY. ANTIBIOTIC. We call the cells of the immune system white blood cells. There are four major types of white blood cells: T cells, B cells, Neutrophils and Macrophage. Macrophage (mack'-row-fage; from the Latin macro = big, phage = eat) are white blood cells that eat germs that have been covered by antibodies. Their job is to patrol the body looking for germs.
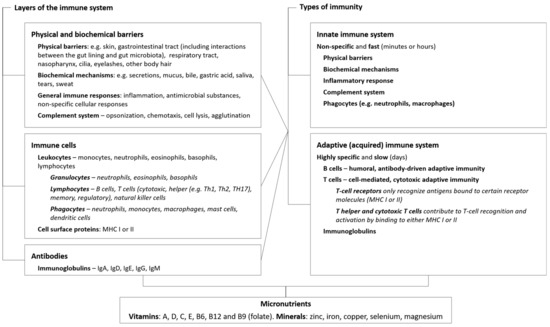
Immune System (and Lymphatic) Use the worksheet above to complete the notes and practice problems included in the worksheet using the series of videos and animations on how the immune system works. Follow the links in order. The videos and links were selected to help you understand how immune system fights pathogens. Lymphatic/Immune System Vocabulary - Key Term Meaning Acquired Immunity Production of antibodies and lymphocytes after exposure to an antigen Adenoids A mass of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx Antibody A protein produced by B cell lymphocytes to destroy antigens Antigen A substance that the body recognizes as foreign; evokes an immune _____ 12. A major function of the humoral immune system is to destroy proteins that are nonself. _____ 13. Both T cells and B cells have receptors that bind specifically to a particular antigen. _____ 14. Helper T cell cytokines stimulate the development of B cells into mature antibody-producing cells. _____ 15. Students know the role of phagocytes, B-lymphocytes, and T-lymphocytes in the immune system. "Phagocytes move, amoeba-like, through the circulatory system, consuming waste and foreign material, such as aged or damaged blood cells and some infectious bacteria and viruses. Two broad types of lymphocytes (a class of white blood cells) originate ...
We call the cells of the immune system white blood cells. There are four major types of white blood cells: macrophage, Neutrophils, T cells, and b cells. Macrophage (mack'-row-fage; from the latin macro = big, phage = eat) are white blood cells that eat germs that have been covered by antibodies. Their job is to patrol the body looking for germs. Immune System: Key Words Worksheet. Students match immune system keywords to their definitions. Answers on second sheet. Suitable for KS5 Biology students. Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. This tutorial provides an overview of the immune system, concentrating on the roles played by B and T lymphocytes, and on the antigen-presentation system. All animals possess a nonspecific defense system called the innate immune system, which includes macrophages in mammals. Vertebrates have an additional powerful immune ... Show more Turning On the Immune System A "lock-and-key" mechanism mobilizes the immune system. When a macrophage inserts a broken envelope fragment into the receptor site of a special kind of white blood cell called a T4 lymphocyte, the whole immune system is readied for action. Like a key turning a lock, the virus fragment turns on the T4's
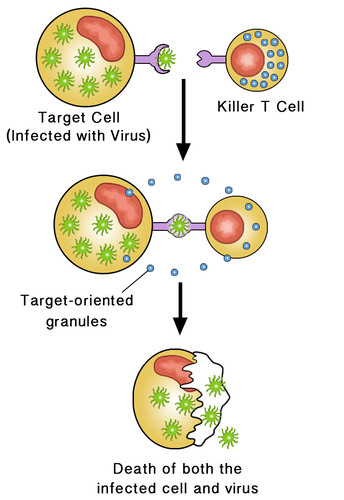
Define innate immune system. Where are the cells of the adaptive immune system found in humans? Watch the video on slide 3 and answer the following. How do B cells react to antigens? Which cells conduct the immune system? Which immune cells kill infected cells? What is the purpose of humoral immunity? How does antibody specificity arise?
Read through the "Introduction," "The immune system -- three lines of defense" and "First line of defense - nonspecific barriers" and answer questions 1-3. Define pathogen and list 4 types of pathogens. Define antigen and give 3 examples of common antigens. What is the purpose of the first line of defense? Is it general or specific?
KEY CONCEPTS 31.1 Pathogens and Human Illness Germs cause many diseases in humans. 31.2 Immune System The immune system consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections. 31.3 Immune Responses The immune system has many responses to pathogens and foreign cells. 31.4 Immunity and Technology
Washing your hands often (1) is the best way to avoid infections and help keep your immune system healthy. You can also keep your immune system strong by (2) eating a nutritious diet, (3) exercising and being active every day, (4) getting enough sleep each night, and (5) visiting a doctor regularly.
While labeling the functions of their cell organelles, students compare their cells to find organelles that are: (1) common to all cells, and (2) unique to each cell type. Finally, they deduce their cell's identity.
Answer Key For Immune System ... accompanying worksheet guides students exploration, lymphatic system and immunity answers and question anatomy amp physiology ch 22 according to prof larson ... are a type of white blood cell the immune system and how they work together to protect
Howard Hughes Medical Institute 2007 Holiday Lectures on Science Cells of the Immune System—Student Worksheet Answer the following questions as you proceed through the activity slides. 1. Name one type of cell involved in each of the following processes: a.
invade cells and to multiply once inside of cells. Section 40-2 The Immune System(pages 1034-1040) This section describes the body's defenses against disease-causing organisms and explains what immunity is. Nonspecific Defenses(pages 1034-1035) 1. The body's primary defense against pathogens is the .
Lesson 3: The Adaptive Immune System While focusing on the structure and function of the adaptive immune system, students compare the innate and adaptive immune systems by examining antigens, B cells, T cells, antibodies, dendritic cells, molecules and processes.
Cells of the Immune System—Student Worksheet . Answer the following questions as you proceed through the activity slides. 1. Name one type of cell involved in each of the following processes: a. Innate immunity: _____ b.
3. The dendritic cell then transport the virus to a lymph node. 4. In the lymph node, there are specialized immune cells, and that is where the immune response to HIV begins. At this point, B cells interact with the virus and those B cells - because of the ability to recognize HIV - will transformed into a cell called the plasma cell.
Cells of the Immune System… These include all of the white blood cells (aka leukocytes), some of which appear "granular"… Granulocytes Neutrophils • phagocytes w/strangely shaped nuclei, poorly stained granular vesicles Basophils • release histamine, other mediators of inflammation, vesicles bind basic dyes Eosinophils
Immune System. Quiz Answer Key. 1. The. immune. system protects your body from sickness and germs. 2. Leukocytes. are white blood cells that seek out and destroy organisms or substances that can . cause disease. 3. Lymph nodes. are glands that work like filters to remove germs. They’re found in your neck, armpit, and other areas. 4.
Immune Cells and Their Products The immune system stockpiles a huge arsenal of cells, not only lymphocytes but also cell-devouring phagocytes and their relatives. Some immune cells take on all comers, while others are trained on highly specific targets. To work effectively, most immune cells need the cooperation of their comrades.
"The Lord of the Immune System" worksheet (with answer key & instructor notes) that complements the podcast bearing the same name. During the spring 2010 semester, the podcast and associated worksheet were used as an extra-credit activity in the BIO152 laboratory setting.
Interpret data and compare to predicted outcomes. Describe cellular and humoral immunity. Draw the HIV virus structure and describe the function of each component. Describe the interaction of the HIV virus with the immune system. Differentiate between resistance and immunity as mechanisms of protection against a foreign particle.






























0 Response to "43 cells of the immune system student worksheet answer key"
Post a Comment